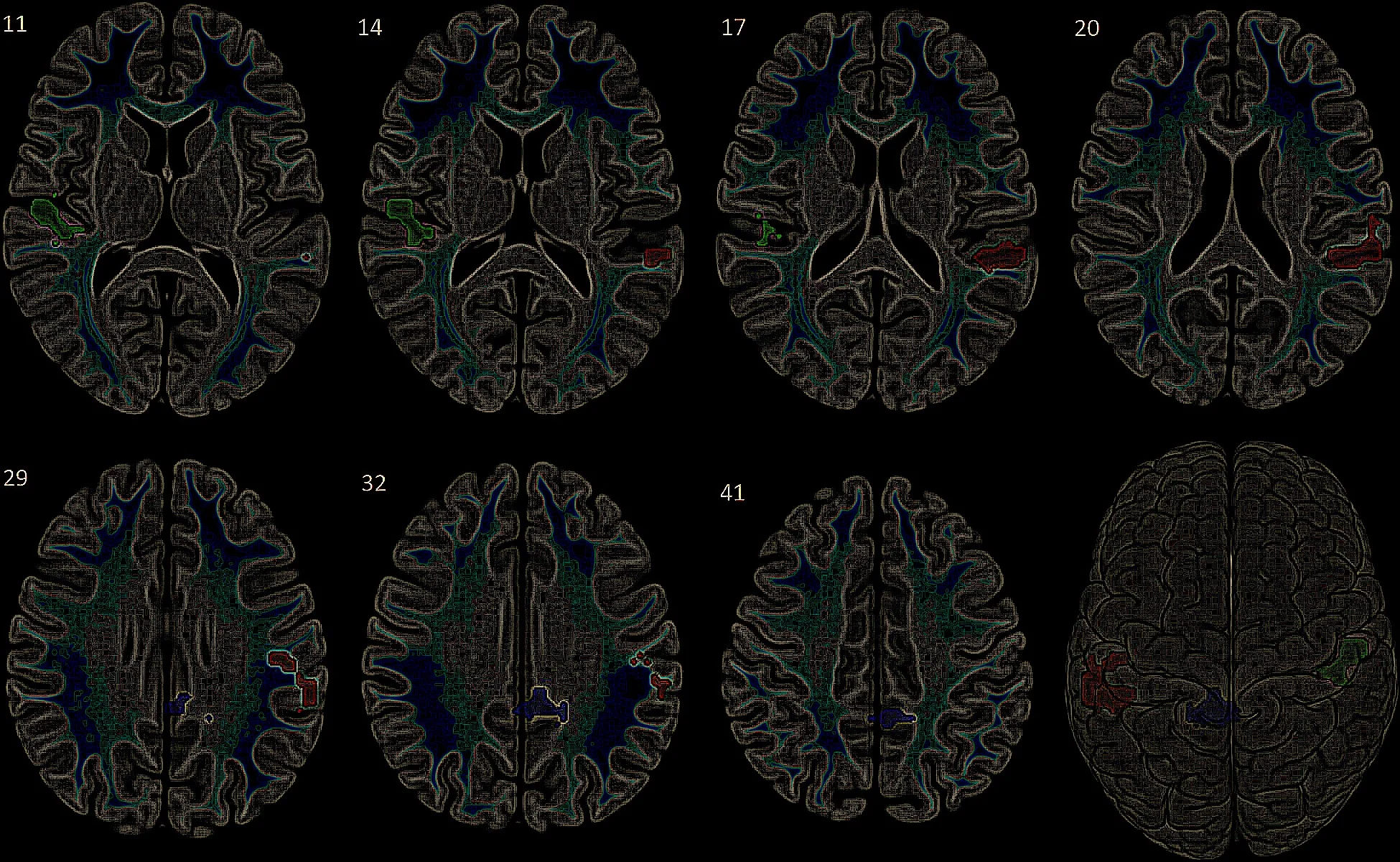
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) represents a highly heterogeneous group of neurodevelopmental conditions defined by core symptoms of impaired social communication and restricted, repetitive behaviors. Severe autism cases, which often include intellectual disability, epilepsy, and profound functional impairments, remain particularly resistant to existing therapeutic interventions. Recent genomic discoveries—many spearheaded by Silvia De Rubeis and colleagues—have highlighted the critical role of synaptic, transcriptional, and chromatin regulatory pathways in ASD. These insights have shifted focus toward a mechanistic understanding of ASD at the molecular level.
At the same time, circadian biology has emerged as a central regulator of neurodevelopment, synaptic plasticity, and behavior. Circadian rhythms, orchestrated by transcriptional–translational feedback loops (TTFLs) in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), regulate thousands of genes involved in metabolism, neurotransmission, and DNA repair. Disruption of these rhythms exacerbates excitatory–inhibitory imbalance, a hallmark of ASD pathophysiology.
The convergence of circadian regulation, time cell dynamics, and ASD genetics creates a promising landscape for therapeutic innovation. A precision medicine framework that incorporates circadian biology could enable the rational design of novel drugs targeting oscillatory mechanisms at the molecular level.
Peter De Ceuster. (2026). Integrating Circadian Rhythm and Neurobiology in Precision Medicine: A Novel Approach for Treating Severe Autism Through the Exploration of Time Cells and Genetic Mechanisms
Excerpt from: Integrating Circadian Rhythm and Neurobiology in Precision Medicine: A Novel Approach for Treating Severe Autism Through the Exploration of Time Cells and Genetic Mechanisms by P. De Ceuster
© All rights reserved. Do not distribute. (Publication: Integrating Circadian Rhythm and Neurobiology in Precision Medicine: A Novel Approach for Treating Severe Autism Through the Exploration of Time Cells and Genetic Mechanisms)